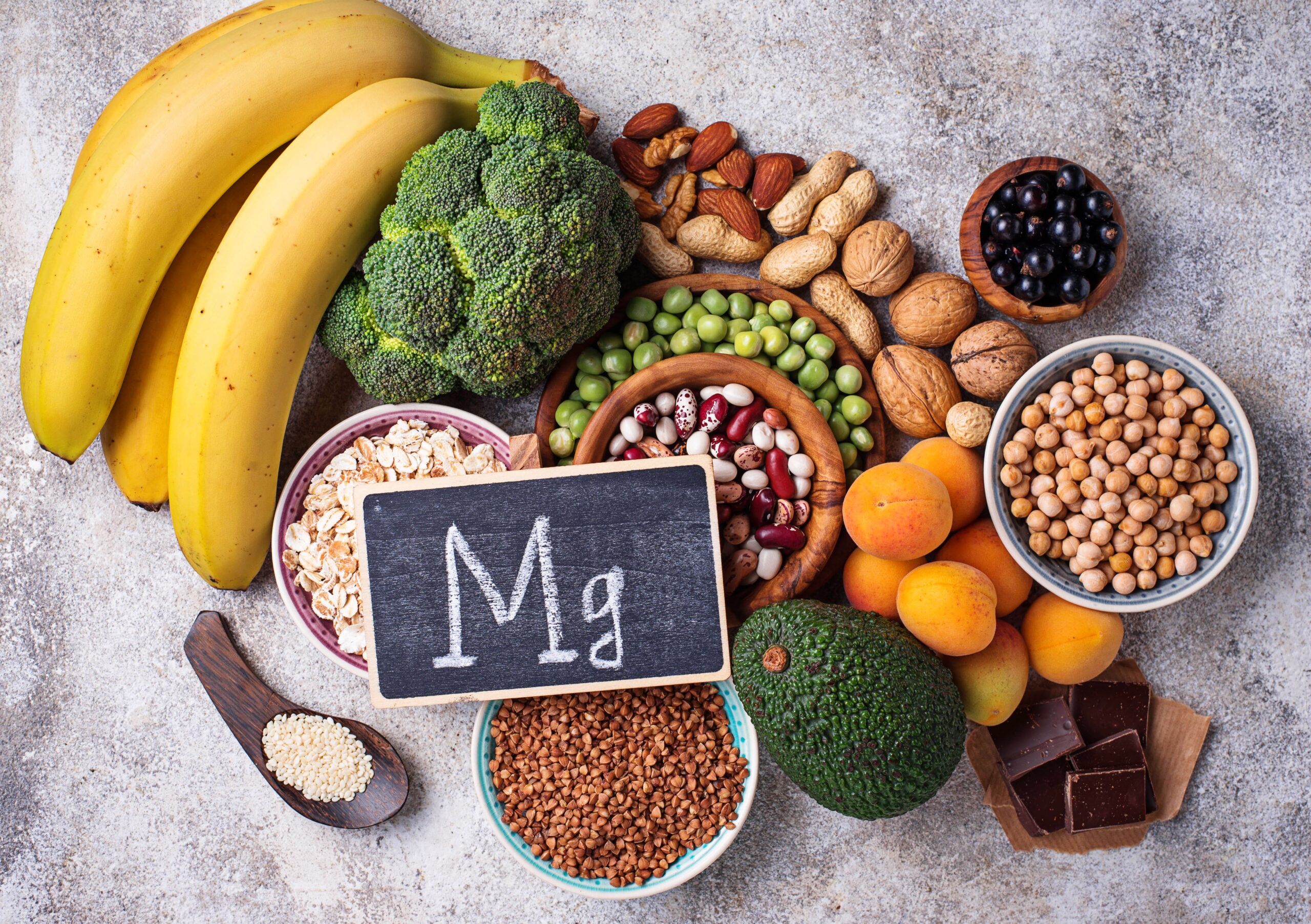
Magnesium citrate, a common supplement form, boasts high bioavailability. The citrate component enhances absorption in the digestive tract, making it an effective choice for individuals looking to address magnesium deficiency promptly.
Due to its favorable absorption profile, magnesium citrate is a popular choice in dietary supplements. It is widely utilized to support magnesium levels in individuals with dietary insufficiencies or those experiencing conditions that hinder magnesium absorption.
While magnesium oxide contains a high percentage of elemental magnesium, its absorption can be challenging. The body may not effectively absorb and utilize magnesium from this form, leading to lower bioavailability compared to other magnesium compounds.
Magnesium oxide occurs in nature, and some magnesium-rich foods contain this form. However, reliance on natural sources alone may not provide sufficient magnesium for optimal health due to absorption challenges associated with magnesium oxide.
Magnesium plays a pivotal role in neuromuscular transmission, influencing the communication between nerves and muscles. Adequate magnesium levels facilitate the smooth transmission of signals, preventing muscle spasms and promoting proper muscle function.
Magnesium oxide occurs in nature, and some magnesium-rich foods contain this form. However, reliance on natural sources alone may not provide sufficient magnesium for optimal health due to absorption challenges associated with magnesium oxide.
Magnesium plays a pivotal role in neuromuscular transmission, influencing the communication between nerves and muscles. Adequate magnesium levels facilitate the smooth transmission of signals, preventing muscle spasms and promoting proper muscle function.
Magnesium is essential for muscle contraction. It works in concert with calcium to regulate muscle contractions and relaxations. Insufficient magnesium can lead to muscle cramps, spasms, and increased susceptibility to muscular injuries.
Magnesium is a cofactor in the synthesis of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the primary energy currency of cells. Its presence is vital for the enzymatic reactions that convert nutrients into ATP, ensuring a steady supply of energy for cellular processes.
Beyond ATP synthesis, magnesium is involved in the transfer and utilization of energy within cells. It supports the function of various enzymes critical for metabolic pathways, influencing overall energy production and utilization in the body.
Chromium absorption is influenced by various factors, including the form in which it is consumed, individual health conditions, and interactions with other minerals. Absorption is generally limited, and factors such as low gastric acidity and the presence of certain compounds may impact the body’s ability to absorb chromium efficiently.
Enhancing chromium absorption involves dietary strategies such as consuming vitamin C-rich foods, avoiding excessive intake of iron and calcium during chromium-rich meals, and maintaining a generally healthy and varied diet to optimize the body’s utilization of this essential mineral.
Insufficient magnesium levels may lead to muscle cramps and spasms. Magnesium is essential for proper muscle function, and its deficiency can disrupt the delicate balance between nerve and muscle, resulting in discomfort and involuntary contractions.
Magnesium is crucial for bone health, working synergistically with calcium and vitamin D. A deficiency in magnesium can compromise bone density and mineralization, contributing to conditions like osteoporosis and increasing the risk of fractures.
Magnesium deficiency has been linked to cardiovascular issues, including hypertension and irregular heart rhythms. Magnesium is vital for maintaining the proper function of the heart and blood vessels, and its deficiency may contribute to cardiovascular complications. Addressing magnesium deficiency is essential for mitigating these potential health risks.
Magnesium supplementation, under medical guidance, is a common approach to address deficiencies. Various magnesium forms, including citrate and glycinate, are available in supplements to enhance absorption and utilization.
Prioritizing magnesium-rich foods such as leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and whole grains ensures a balanced intake. Dietary diversity and awareness of magnesium content in foods contribute to maintaining optimal magnesium levels.
In conclusion, understanding the forms, functions, and potential consequences of magnesium deficiency highlights its vital role in maintaining health. Whether through supplementation or dietary choices, ensuring adequate magnesium levels is paramount for overall well-being, emphasizing its profound impact on various physiological processes.
COPYRIGHTS © 2026 VITAMIN SCIENCES.
ALL RIGHTS ARE RESERVED.