
Vitamin C, chemically known as ascorbic acid, is a water-soluble vitamin essential for human health. Its chemical structure consists of six carbon atoms, six oxygen atoms, and eight hydrogen atoms. This molecular arrangement allows it to act as a powerful antioxidant, neutralizing harmful free radicals in the body.
Vitamin C is naturally present in a variety of fruits and vegetables. Citrus fruits like oranges, lemons, and grapefruits are well-known sources. Additionally, vegetables like broccoli, spinach, and bell peppers contain significant amounts of Vitamin C. Berries, tomatoes, and even some tropical fruits like kiwi, guava, and mango are rich sources, ensuring a diverse range of options for individuals to maintain their Vitamin C intake.
The recommended daily allowance of Vitamin C varies based on factors such as age, gender, and life stage. However, for most adults, the RDA is typically around 90 milligrams per day. Pregnant and breastfeeding women might require slightly higher amounts. It's crucial to obtain this vitamin through a balanced diet, as the body does not store excess Vitamin C, emphasizing the importance of consistent intake from food sources or supplements if necessary.
In joints, it acts as a cushion, facilitating smooth movements, while in blood vessels, it maintains their strength and flexibility, promoting proper circulation. Adequate collagen levels are crucial for joint mobility, cardiovascular health, and youthful skin. Vitamin C aids in wound healing and tissue repair by promoting collagen synthesis.
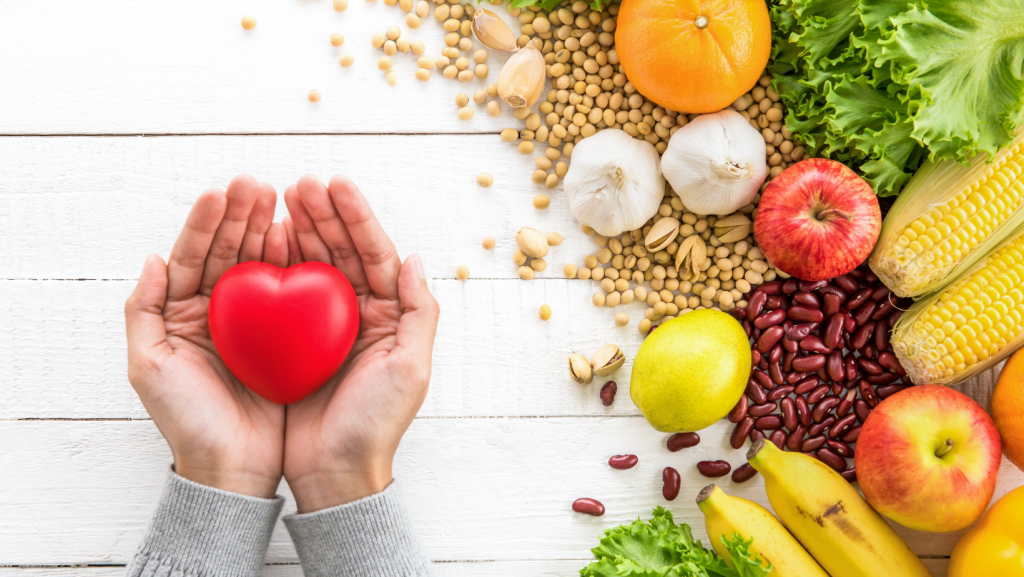

Vitamin C contributes to heart health by aiding in the relaxation of blood vessels, which lowers blood pressure. Additionally, it helps regulate cholesterol levels by reducing LDL cholesterol and increasing HDL cholesterol, the "good" cholesterol. By optimizing these factors, Vitamin C significantly reduces the strain on the cardiovascular system, promoting a healthy heart
Many studies have demonstrated the correlation between adequate Vitamin C intake and a reduced risk of heart disease. Research has shown that individuals with higher Vitamin C levels in their bloodstream have a lower risk of stroke and heart disease. These studies highlight the importance of including Vitamin C-rich foods in the diet to maintain cardiovascular health.
COPYRIGHTS © 2026 VITAMIN SCIENCES.
ALL RIGHTS ARE RESERVED.