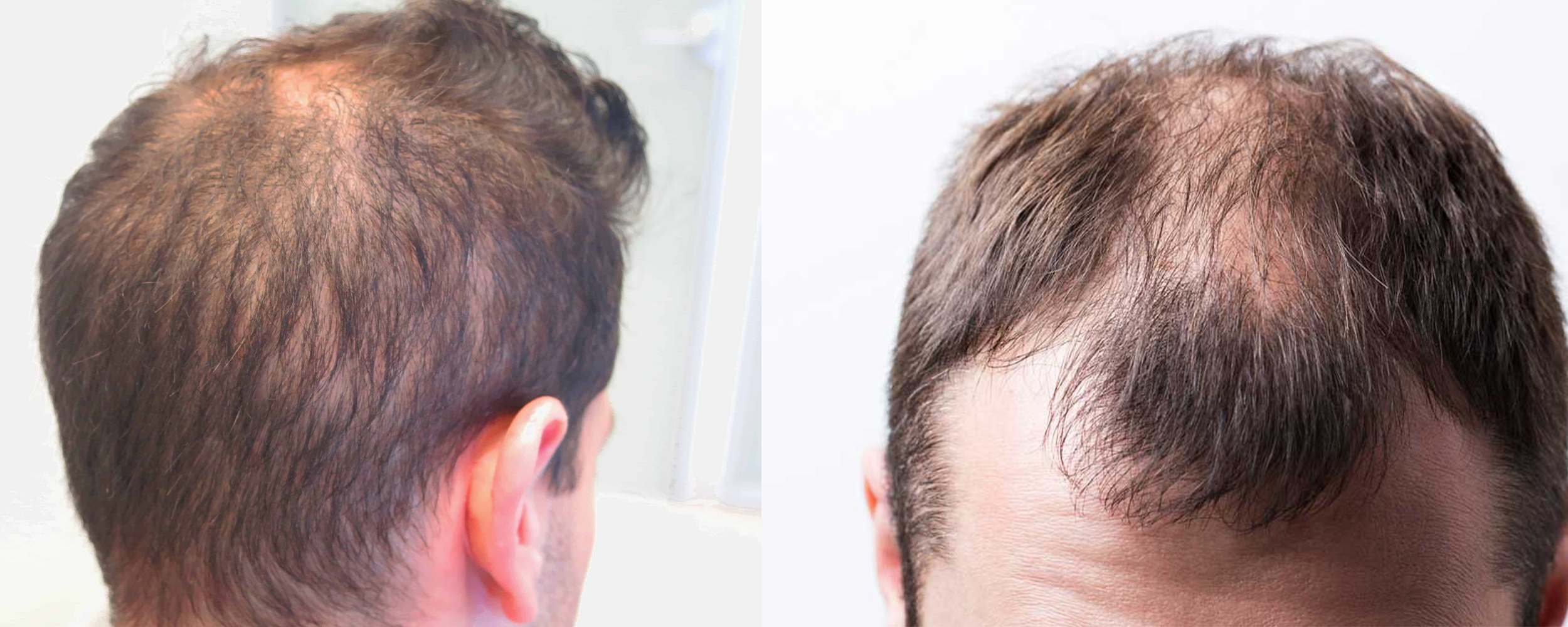

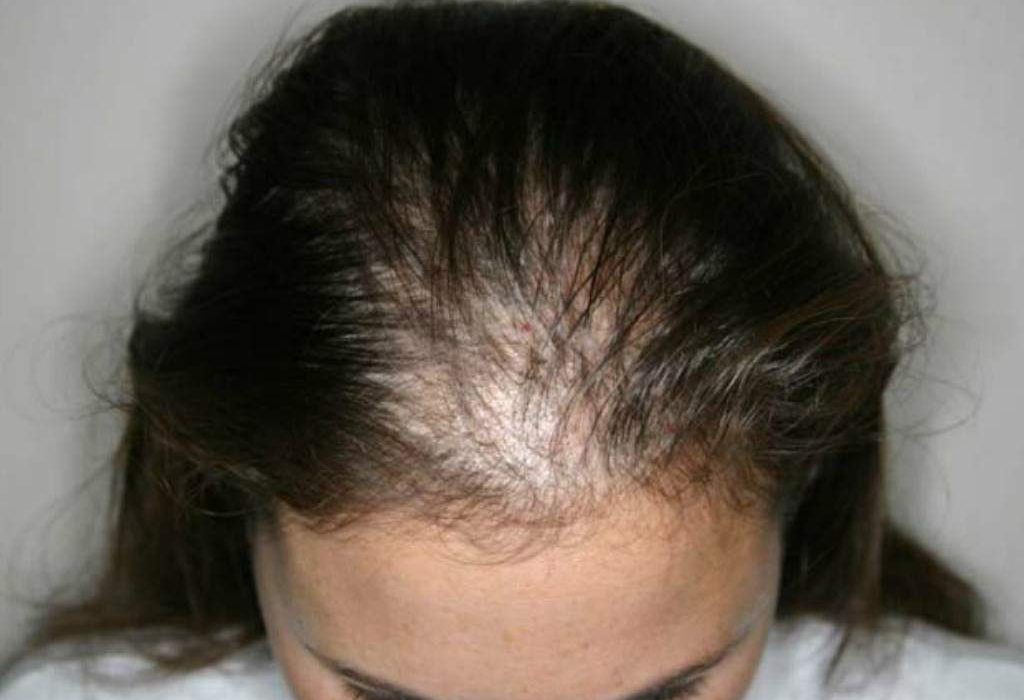
Individuals with diffuse hair loss often experience increased daily hair shedding. This can be observed on pillows, in the shower drain, or while combing or brushing hair.
One of the primary symptoms of diffuse hair loss is the noticeable thinning of hair all over the scalp rather than specific bald patches.
Hair appears less dense, and the overall volume of hair decreases, making it difficult to style hair as before.
Hair strands may become weaker, finer, and more prone to breakage. This can lead to a lack of vitality and luster in the hair.
Due to thinning, the scalp becomes more visible, especially under bright lights or when hair is wet.
Hair texture may become limp, lifeless, and difficult to manage. It may lose its natural bounce and shine.
Diffuse hair loss can result in slower hair growth, with new hair regrowth being thinner and weaker than before.
The scalp might become more sensitive or itchy, indicating an imbalance or irritation in the hair follicles.
Diffuse hair fall, or telogen effluvium, can be triggered by various factors, each contributing to an accelerated shedding of hair from the scalp. Some common causes include:
Fluctuations in hormones due to pregnancy, childbirth, menopause, or thyroid disorders can disturb the hair growth cycle, causing excessive shedding.
Poor diet and nutritional imbalances, particularly deficiencies in iron, biotin, zinc, and other essential vitamins and minerals, can weaken hair follicles and lead to diffuse hair fall.
High stress levels, whether from personal issues, work-related pressure, or significant life changes, can disrupt the hair growth cycle, leading to diffuse hair loss. Emotional trauma, such as the loss of a loved one, can also be a significant factor.
Drastic weight loss through crash diets or extreme calorie restriction can shock the body and result in diffuse hair loss.
Some medications, including anticoagulants, antidepressants, and certain blood pressure drugs, may list hair loss as a side effect, leading to diffuse shedding.
Certain medical conditions like autoimmune disorders, chronic illnesses, and cancer can cause hair shedding. Additionally, treatments like chemotherapy and radiation therapy can lead to widespread hair loss.
Overusing hair styling tools, frequent chemical treatments, and tight hairstyles that pull on the hair can weaken follicles, causing hair to fall out more quickly.
Essential for red blood cell formation, B12 aids in oxygen transport to the scalp, promoting hair growth and preventing hair loss.
Acts as an antioxidant, supporting the production of sebum, which nourishes the scalp and keeps hair healthy.
Often hailed as the "hair vitamin," biotin strengthens hair strands and prevents breakage, contributing to fuller, thicker hair.
Boosts collagen production, a crucial protein for hair structure, ensuring stronger and healthier hair.
Vital for the hair follicles' health, adequate vitamin D levels can help reduce hair shedding and promote regrowth.
An antioxidant that enhances scalp circulation, promoting a healthy environment for hair growth.
Weakens hair, leading to shedding.
Results in brittle, thinning hair.
Weakens hair strands, causing breakage.
Disrupts the hair growth cycle, increasing hair loss.
This can lead to hair thinning and loss.
Impairs scalp circulation and affects hair follicles.
Contributes to hair loss by affecting essential proteins.
COPYRIGHTS © 2026 VITAMIN SCIENCES.
ALL RIGHTS ARE RESERVED.